BioMat WUT
polymers and materials for bioapplications
Latest news
-

Our Research Highlighted on the Journal Cover
Our recent paper, published in Macromolecular Bioscience, was highlighted on the journal cover. The cover features the polymeric structure we investigated and Candida albicans cells affected by this novel antibacterial agent. Kudos to all the authors! Kurzyna, J. M.; Kopiasz, R. J.; Paul, M.; Flont, M.; Baranowska, P.; Mierzejewska, J.; Drężek, K.; Tomaszewski, W.; Jastrzębska,
-

Lactide oligomers modified with linear polyethyleneimine for antibacterial coatings
by Iuliano, A.*; Kukuć, M.; Pachla, J.; Jańczewski, D.; Mierzejewska J.; Drężek, K. Polym.Chem. 2024 https://doi.org/10.1039/d4py00605d Lactide oligomers were synthesized in the presence of glycidol via ring opening solution polymerization and used in the addition reaction with linear polyethyleneimine (L-PEI). Detailed analysis of the lactide oligomerswas conducted using 1H NMR, GPC and MALDI-ToF. L-PEI with
-

Unlocking the Potential: PEGylation and Molecular Weight Reduction of Ionenes for Enhanced Antifungal Activity and Biocompatibility
by Kurzyna, J. M.; Kopiasz, R. J.; Paul, M.; Flont, M.; Baranowska, P.; Mierzejewska, J.; Drężek, K.; Tomaszewski, W.; Jastrzębska, E.; Jańczewski, D. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 24(9) 2400032. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.202400032 Numerous synthetic polymers, imitating natural antimicrobial peptides, have demonstrated potent antimicrobial activity, positioning them as potential candidates for new antimicrobial drugs. However, the high activity of these
-
PhD scholarship available – deadline extended to 15 of August 2024
!!Important update!!, application deadline is extened to 15 August 2024 **Call for Applications for a Doctoral Scholarship in a project founded by National Science Centre Poland** **Controlled Post-Polymerization Modification Method and Its Application in Producing Polymer Agents That Disrupt Cell Wall Structure (ConPPM)** Chemical modification of polymers after the polymerization stage (post-polymerization modification, PPM) is
-

L-PTMI-Co-L-PEI Copolymers Obtained through Copolymerization of Cyclic Imino Ethers and Their Chain Modification: Antibacterial Properties and Cytotoxicity
by Pachla, J.; Kowalczyk, S.; Tomaszewski, W.; Gnyszka, A.; Flont, M.; Grzechnik, E.; Drężek, K.; Plichta, A.; Mierzejewska, J.; Jastrzębska, E.; Jańczewski, D. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 213, 113088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2024.113088 Polymeric antimicrobial agents are intensively investigated as potential novel antibiotics. In this work we use copolymerization of 2-propyl-2-oxazine (PrOzi) and 2-methyl-2-oxazoline (MeOx) combined with hydrolysis
-

Membrane Lytic Activity of Antibacterial Ionenes, Critical Role of Phosphatidylcholine (PC) and Cardiolipin (CL)
by Kozon-Markiewicz, D.; Kopiasz, R. J.; Głusiec, M.; Łukasiak, A.; Bednarczyk, P.; Jańczewski, D. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 229, 113480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113480 Understanding the mechanism by which an antibacterial agent interacts with a model membrane provides vital information for better design of future antibiotics. In this study, we investigated two antibacterial polymers, hydrophilic C0-T-p and
-

Highly Potent Antibacterial Agents with Activity and Toxicity Modulated by the Polymer Molecular Weight
by Pachla, J.; Kopiasz, R. J.; Marek, G.; Tomaszewski, W.; Głogowska, A.; Drężek, K.; Kowalczyk, S.; Podgórski, R.; Butruk-Raszeja, B.; Ciach, T.; Mierzejewska, J.; Plichta, A.; Augustynowicz-Kopeć, E.; Jańczewski, D. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24 (5), 2237–2249 https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00139 Cationic polymers have been extensively investigated as apotential replacement for traditional antibiotics. Here, we examined theeffect of molecular weight
-

Main-Chain Flexibility and Hydrophobicity of Ionenes Strongly Impact Their Antimicrobial Activity: An Extended Study on Drug Resistance Strains and Mycobacterium.
by Kopiasz, R. J.; Zabost, A.; Myszka, M.; Kuźmińska, A.; Drężek, K.; Mierzejewska, J.; Tomaszewski, W.; Iwańska, A.; Augustynowicz-Kopeć, E.; Ciach, T.; Jańczewski, D. RSC Adv. 2022, 12 (40), 26220–26232 https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA04121A The spread of antibiotic-resistant pathogens and the resurgence of tuberculosis disease are major motivations to search for novel antimicrobial agents. Some promising candidates in
-

Influence of PEG Subunit on the Biological Activity of Ionenes: Synthesis of Novel Polycations, Antimicrobial and Toxicity Studies
by Kopiasz, R. J.; Kulbacka, N.; Drężek, K.; Podgórski, R.; Łojszczyk, I.; Mierzejewska, J.; Ciach, T.; Augustynowicz‐Kopeć, E.; Głogowska, A.; Iwańska, A.; Tomaszewski, W.; Jańczewski, D. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22 (7), 2200094. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mabi.202200094 An alarming increase of antibiotic resistance among pathogens creates an urgent need to develop new antimicrobial agents. Many reported polycations show high
-
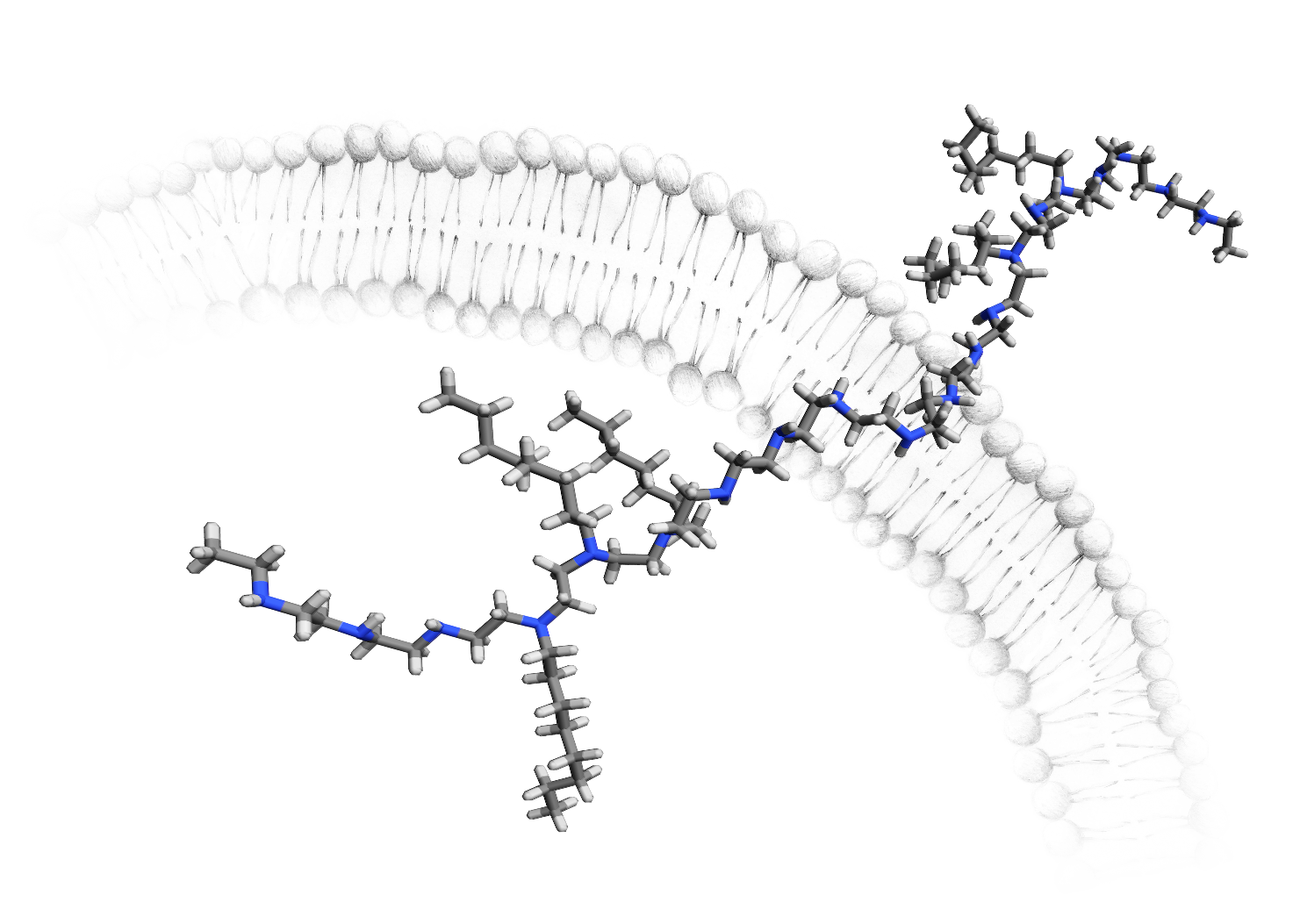
Controlled post-polymerization modification method and its application for construction of macromolecular membrane-lytic agents
The post-polymerization modification (PPM) is an approach to change the structure of a polymer at the final stage of synthesis when the polymerization process is already completed. Project funded under the OPUS scheme by National Science Center, Poland.